Transatlantic AI Divide: Trump Administration Vs. European Regulations

Table of Contents
The Trump Administration's Approach: A Laissez-Faire Stance
The Trump administration prioritized fostering AI innovation, advocating for minimal government intervention. This approach, often described as laissez-faire, aimed to maintain US competitiveness in the global AI race, believing that excessive regulation would stifle innovation.
Emphasis on Innovation over Regulation
The core tenet of the Trump administration's AI policy was to let the free market drive innovation. This resulted in:
- Limited federal regulations on AI development and deployment: Unlike the EU's proactive approach, the US largely relied on self-regulation and industry best practices. This hands-off approach fostered a rapid pace of development, particularly in areas like deep learning and natural language processing.
- Focus on promoting private sector investment and research: Significant government funding was channeled towards AI research through grants and tax incentives, primarily targeting private sector companies and research institutions. This spurred private investment and competition.
- Emphasis on self-regulation and industry best practices: The administration encouraged industry groups to develop their own ethical guidelines and standards for responsible AI development. This approach, while promoting agility, lacked the uniformity and enforcement mechanisms of a centralized regulatory body.
- Concerns over stifling innovation through excessive regulation: A primary argument against stricter regulations was the fear that it would hinder the progress of AI technology and place the US at a competitive disadvantage against nations with less stringent rules.
National Security Concerns and AI Development
While prioritizing minimal regulation, the Trump administration recognized the critical role of AI in national security. This resulted in:
- Increased funding for AI research related to defense and national security: Significant investments were made in AI technologies for military applications, cybersecurity, and intelligence gathering.
- Focus on AI talent acquisition and retention: Efforts were made to attract and retain top AI talent from around the world, recognizing the importance of a skilled workforce for national security.
- Initiatives to counter the use of AI by adversarial nations: The administration focused on developing countermeasures against the use of AI by rival countries, particularly in areas like cyber warfare and disinformation campaigns.
- Limited public transparency regarding AI development in the defense sector: Much of the AI research and development within the defense sector remained opaque, raising concerns about accountability and potential misuse of the technology.
The European Union's Approach: A Focus on Ethics and Data Protection
In stark contrast to the US approach, the European Union has prioritized ethics and data protection in its AI strategy. This approach is heavily influenced by the GDPR and a strong emphasis on societal well-being.
The GDPR's Impact on AI Regulation
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), enacted in 2018, fundamentally reshaped the EU's approach to data handling and subsequently, AI regulation. This led to:
- Stricter rules on data collection, processing, and storage for AI systems: The GDPR places stringent requirements on how personal data can be used for training and deploying AI systems, emphasizing consent and data minimization.
- Greater transparency requirements for AI algorithms and decision-making processes: The "right to explanation" under the GDPR demands that individuals understand how AI systems make decisions that affect them.
- Emphasis on user consent and data control: Individuals have more control over their personal data, making it more challenging for companies to use it for AI development without explicit consent.
- Higher penalties for data breaches and violations of privacy rights: The GDPR introduced significant fines for companies that fail to comply with data protection rules, creating a strong incentive for compliance.
Ethical Guidelines and AI Development
The EU has actively developed ethical guidelines for AI, going beyond mere data protection to address broader societal concerns:
- Development of ethical frameworks for responsible AI development: The EU has published various ethical guidelines and recommendations for the development and deployment of AI, focusing on principles like fairness, accountability, and transparency.
- Initiatives to address algorithmic bias and discrimination: The EU recognizes the potential for AI systems to perpetuate existing societal biases and is working to develop methods to mitigate this risk.
- Emphasis on human oversight and control over AI systems: The EU favors a human-centered approach to AI, ensuring that humans retain control over critical decisions made by AI systems.
- Increased investment in research on the societal impacts of AI: The EU is funding research projects exploring the broader societal implications of AI, including its impact on employment, social equity, and democratic processes.
The AI Act: A More Formalized Regulatory Framework
The EU's commitment to responsible AI is further solidified by the proposed AI Act, a landmark piece of legislation that will likely establish a more comprehensive and stringent regulatory framework:
- Risk-based approach: The AI Act categorizes AI systems based on their risk level, with higher-risk systems facing stricter regulatory scrutiny.
- Prohibition of certain AI applications: The Act proposes a ban on certain AI applications deemed unacceptable, such as social scoring systems and predictive policing tools that lack sufficient safeguards.
- Stricter requirements for high-risk AI systems: High-risk AI systems, like those used in healthcare or transportation, will be subject to rigorous testing, auditing, and oversight.
Consequences of the Transatlantic AI Divide
The differing regulatory approaches between the US and EU have several far-reaching consequences:
Differing Levels of Innovation
The laissez-faire approach in the US might foster faster innovation in certain areas, while the EU's focus on ethics and data protection could lead to slower development but potentially more responsible and trustworthy AI systems. This creates a complex landscape where neither approach is definitively superior.
International Data Flows and Collaboration
The regulatory discrepancies create challenges for international data flows and collaboration on AI projects. Companies operating across the Atlantic must navigate complex legal requirements, potentially hindering cross-border data sharing and collaboration.
Global AI Standards
The divergence in approaches complicates the development of global AI standards and norms. The lack of harmonization could lead to inconsistencies in AI regulation across different jurisdictions, creating confusion and potentially hindering the global adoption of AI.
Conclusion
The Transatlantic AI Divide, shaped by the contrasting approaches of the Trump administration and the European Union, presents significant challenges and opportunities for the future of AI. Understanding the differing regulatory landscapes is crucial for businesses, researchers, and policymakers alike. Navigating this Transatlantic AI Divide successfully requires a nuanced understanding of both approaches and a commitment to developing ethical and effective AI governance frameworks that balance innovation with responsible development. Are you prepared to understand and navigate the complexities of the Transatlantic AI Divide and ensure your organization is compliant with both US and EU regulations?

Featured Posts
-
 Pentagon In Turmoil Exclusive Interview Reveals Leaks And Internal Disputes
Apr 26, 2025
Pentagon In Turmoil Exclusive Interview Reveals Leaks And Internal Disputes
Apr 26, 2025 -
 White House Cocaine Incident Secret Service Concludes Investigation
Apr 26, 2025
White House Cocaine Incident Secret Service Concludes Investigation
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Todays Stock Market Dow Futures Chinas Economic Stimulus And Trade Uncertainty
Apr 26, 2025
Todays Stock Market Dow Futures Chinas Economic Stimulus And Trade Uncertainty
Apr 26, 2025 -
 The Florida I Love A Cnn Anchors Travelogue
Apr 26, 2025
The Florida I Love A Cnn Anchors Travelogue
Apr 26, 2025 -
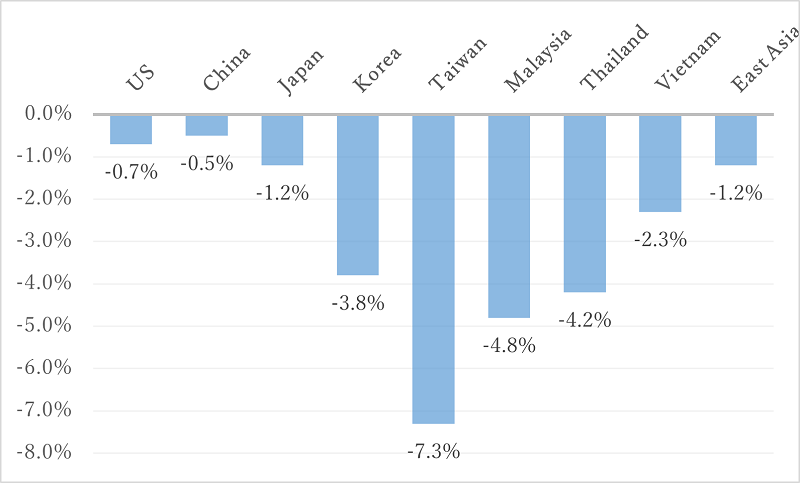 Us China Trade War Impact Dow Futures And Economic Outlook
Apr 26, 2025
Us China Trade War Impact Dow Futures And Economic Outlook
Apr 26, 2025
