Russian Gas Phaseout: The EU's Spot Market Strategy
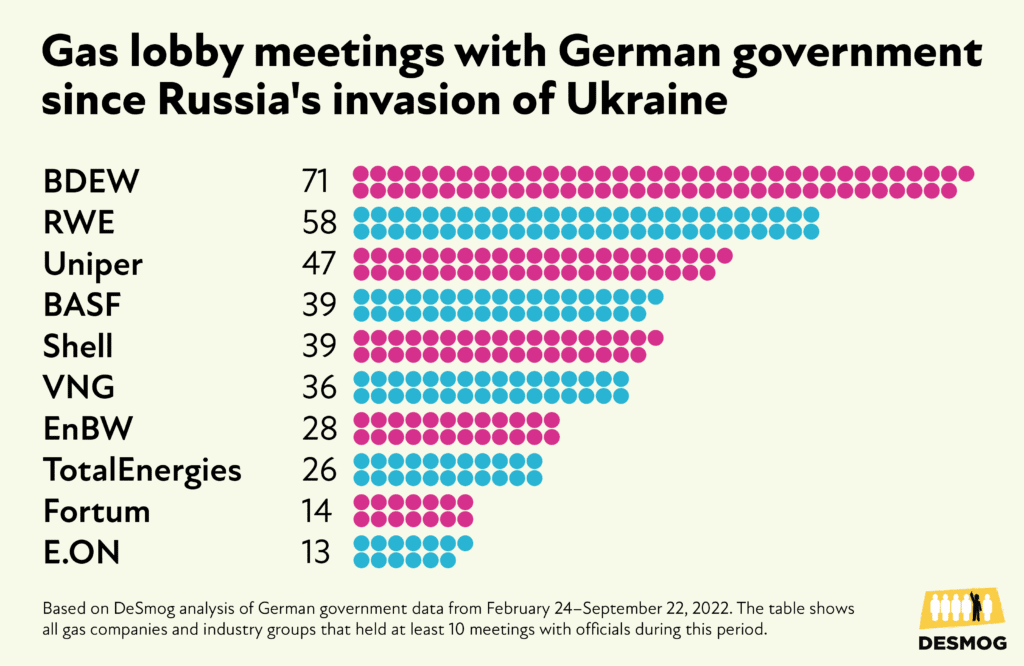
Table of Contents
The Urgency of Diversifying Gas Supplies
The EU's decision to phase out Russian gas stems from a confluence of factors. The ongoing war in Ukraine dramatically highlighted the vulnerability of relying on a single, politically volatile supplier. Energy security concerns, once a secondary consideration, have become paramount, demanding a swift and comprehensive diversification of energy sources. The dependence on Russian gas exposed the EU to geopolitical leverage, threatening both economic stability and national security. The war also sent shockwaves through global energy markets, resulting in unprecedented price volatility and creating a critical need for a more resilient and independent energy system.
The impact of the war on gas supplies and prices has been profound. The immediate consequence was a sharp reduction in Russian gas imports, forcing the EU to scramble for alternative sources. This has resulted in:
- Increased reliance on LNG imports: Liquefied natural gas (LNG) has become a vital component of the EU's energy mix, requiring significant investment in import terminals and infrastructure.
- Expansion of pipeline infrastructure from alternative sources: The EU is actively pursuing pipeline projects with countries such as Norway, Azerbaijan, and Algeria to diversify its gas supply routes.
- Acceleration of renewable energy projects: The crisis has accelerated the transition to renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Energy efficiency measures and demand reduction strategies: The EU has implemented measures to improve energy efficiency in buildings, industry, and transportation, along with campaigns to promote energy conservation.
The Role of the Spot Market in the Transition
The spot market for natural gas provides a platform for immediate buying and selling of gas at prevailing market prices. Unlike long-term contracts, which involve pre-agreed quantities and prices over an extended period, the spot market offers flexibility and adaptability to fluctuating demand and supply conditions. This flexibility is crucial for the EU's strategy, allowing it to quickly adjust its gas imports based on real-time market conditions and the availability of alternative sources.
However, the spot market also presents considerable challenges. The most significant is price volatility. Prices can fluctuate dramatically depending on supply and demand, impacting consumer energy bills and creating uncertainty for businesses. Heavy reliance on the spot market also increases the risk of supply disruptions, particularly during peak demand periods.
The successful integration of the spot market requires:
- Mitigation of increased price volatility: This can be achieved through hedging strategies, risk management tools, and potentially the development of regional price benchmarks.
- Addressing potential supply disruptions: Diversification of supply sources, development of strategic gas storage, and robust market oversight mechanisms are crucial.
- Robust market infrastructure: The EU needs to invest in upgrading and expanding its gas infrastructure, including LNG terminals, pipelines, and storage facilities.
- Efficient LNG hubs: Strategic locations for LNG regasification and trading are vital for facilitating smooth spot market operations.
Key Players and Their Strategies in the EU Spot Gas Market
The EU's spot gas market involves a complex interplay of various actors, each with its own strategies for navigating this dynamic landscape. These include:
- Gas producers: Countries like Norway, Qatar, the US, and Algeria play a crucial role in supplying LNG to the EU spot market. Their strategies often involve optimizing production and export capacity to meet fluctuating demand.
- Importers and distributors: These companies are responsible for importing LNG and distributing it across the EU's vast network. Their strategies focus on securing reliable supply chains and managing price risks.
- Consumers: Businesses and households across the EU are consumers of natural gas. Their strategies involve managing energy costs and identifying ways to reduce consumption.
The interactions among these players are characterized by both competition and cooperation. Strategies employed include:
- Strategies of major LNG exporting countries: These often focus on building long-term relationships with EU importers, securing export contracts, and enhancing LNG infrastructure.
- The role of EU institutions: The European Commission plays a pivotal role in market regulation, coordination, and the promotion of energy security.
- The influence of financial institutions: Banks and financial institutions facilitate gas trading, providing financing for infrastructure projects and managing price risks.
- Impact on different EU member states: The impact of spot market dynamics varies significantly depending on a nation's geographical location, infrastructure, and reliance on natural gas.
Challenges and Opportunities for the EU's Spot Market Strategy
The EU's increased reliance on the spot market is not without risk. Price volatility poses a significant challenge, requiring effective mitigation strategies. The potential for supply disruptions, especially during periods of high demand, necessitates robust infrastructure and diversification of supply sources. Moreover, market transparency and fair competition are crucial for preventing market manipulation and ensuring affordable energy prices for consumers.
However, the spot market also presents substantial opportunities. It can foster greater market integration within the EU, driving efficiency and ensuring a more competitive energy market. The EU can leverage the spot market to accelerate the transition towards a more sustainable and secure energy future, reducing its vulnerability to geopolitical instability.
Key steps to enhance the efficiency and resilience of the EU's spot market include:
- Hedging and risk management: Implementing sophisticated risk management strategies can help mitigate price volatility and protect consumers from price shocks.
- Investing in interconnector pipelines: Developing interconnectors between countries strengthens market integration and enhances supply security.
- Regional gas storage facilities: Investing in strategic gas storage can buffer the impact of supply disruptions and price volatility.
- Strengthening regulatory frameworks: Transparent and robust regulatory frameworks are crucial for ensuring fair competition and market transparency.
Securing the EU's Energy Future: A Spot Market Approach to the Russian Gas Phaseout
The EU's strategy to phase out Russian gas hinges on a multifaceted approach, with the spot market playing a pivotal role. While the transition presents considerable challenges—primarily price volatility and potential supply disruptions—the opportunities for a more resilient, diversified, and secure energy system are substantial. Diversifying gas supplies, improving market transparency, and developing robust infrastructure are critical components of the success of this strategy. The EU's ability to navigate the complexities of the spot market will be instrumental in securing a sustainable and affordable energy future for its citizens, free from the political and economic vulnerabilities inherent in heavy reliance on a single supplier. To learn more about the EU's energy policies and the evolving role of the spot market, explore resources from the European Commission's Energy Directorate-General. [Insert link to relevant resource here]

Featured Posts
-
 Analysis Of Teslas Q1 2024 Earnings Impact Of Political Backlash On Net Income
Apr 24, 2025
Analysis Of Teslas Q1 2024 Earnings Impact Of Political Backlash On Net Income
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Are Wildfire Bets The New Normal The Case Of The Los Angeles Fires
Apr 24, 2025
Are Wildfire Bets The New Normal The Case Of The Los Angeles Fires
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Long Term Impact Of Toxic Chemicals From Ohio Train Derailment On Buildings
Apr 24, 2025
Long Term Impact Of Toxic Chemicals From Ohio Train Derailment On Buildings
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Canada Election Conservative Platform Focuses On Tax Cuts And Deficit Control
Apr 24, 2025
Canada Election Conservative Platform Focuses On Tax Cuts And Deficit Control
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Teslas Optimus Robot Production Faces Setbacks Due To Chinas Rare Earth Policies
Apr 24, 2025
Teslas Optimus Robot Production Faces Setbacks Due To Chinas Rare Earth Policies
Apr 24, 2025
