Middle Managers: The Unsung Heroes Of Business Success And Employee Development

Table of Contents
The Bridge Between Leadership and Employees
Middle managers act as a vital conduit, ensuring smooth communication and information flow throughout the organization. Their effectiveness directly impacts employee engagement and overall productivity.
Effective Communication and Information Flow
Middle managers translate upper management directives into actionable tasks for their teams, ensuring everyone understands expectations and objectives. Simultaneously, they act as a crucial feedback loop, conveying employee concerns, suggestions, and performance insights to senior leadership. This two-way communication is critical for maintaining a healthy and productive work environment.
- Examples of effective communication strategies: Regular team meetings, clear and concise written communication, open-door policies, utilizing collaborative tools.
- Overcoming communication barriers: Actively listening to team members, providing regular updates, seeking clarification when needed, fostering a culture of open dialogue.
- Importance of feedback mechanisms: Regular performance reviews, 360-degree feedback, informal check-ins, utilizing employee surveys to gather feedback. This ensures that communication flows effectively in both directions.
Fostering a Positive and Productive Work Environment
Beyond communication, middle managers are responsible for cultivating a positive and productive team culture. This includes promoting collaboration, resolving conflicts, and boosting employee morale. A supportive and engaging work environment fosters higher productivity and employee retention.
- Strategies for team building: Team-building activities, social events, encouraging collaboration on projects, recognizing and rewarding team accomplishments.
- Conflict resolution techniques: Mediation, active listening, facilitating constructive dialogue, finding mutually acceptable solutions.
- Creating a supportive work environment: Offering regular support, providing mentorship, recognizing individual contributions, creating a culture of trust and respect.
- Promoting employee morale: Celebrating successes, acknowledging efforts, providing opportunities for growth and development, ensuring work-life balance.
Driving Performance and Achieving Business Goals
Middle managers play a pivotal role in driving performance and achieving business goals. This involves setting clear expectations, providing regular feedback, and fostering employee development.
Setting Clear Expectations and Providing Performance Feedback
Setting SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) goals is critical. Middle managers must ensure each team member understands their individual contributions to overall objectives. Providing regular feedback – both positive and constructive – is essential for improvement and growth. This includes conducting regular performance reviews.
- Examples of SMART goals: "Increase sales by 15% in the next quarter," "Reduce customer complaints by 10% within six months," "Complete the project by the deadline of December 31st."
- Techniques for effective feedback delivery: Providing specific examples, focusing on behaviors rather than personality, offering suggestions for improvement, creating a safe space for feedback.
- Conducting constructive performance reviews: Using a structured approach, reviewing both strengths and weaknesses, setting goals for future performance, providing opportunities for professional development.
Mentoring and Developing Employees
Middle managers are often the first line of support for employee development. They identify talent, provide mentorship, and facilitate training programs to improve employee skills and career progression. Investing in employee development is a key strategy to improve retention and enhance business success.
- Mentorship strategies: Pairing experienced employees with newer team members, providing regular guidance and support, facilitating networking opportunities, sharing knowledge and expertise.
- Employee training programs: Identifying training needs, recommending relevant courses or workshops, providing opportunities for on-the-job training and skill development.
- Identification of talent: Recognizing high-potential employees, providing challenging assignments, offering opportunities for advancement, supporting career development plans.
- Career development planning: Helping employees define career goals, creating development plans, providing resources and support, facilitating career progression within the organization.
Overcoming Challenges Faced by Middle Managers
Middle managers frequently face significant challenges, including balancing conflicting demands and navigating organizational change. Successfully navigating these obstacles is essential for their effectiveness and the success of their teams.
Balancing Conflicting Demands
Middle managers often juggle multiple priorities, receiving directives from upper management while simultaneously managing the needs and concerns of their teams. Effective time management and prioritization are crucial.
- Time management techniques: Prioritizing tasks, using time-blocking, delegating effectively, utilizing project management tools, setting realistic deadlines.
- Prioritization strategies: Using the Eisenhower Matrix (urgent/important), focusing on high-impact tasks, learning to say "no" to non-essential tasks.
- Delegation skills: Assigning tasks appropriately, providing clear instructions, monitoring progress, offering support and guidance.
- Stress management: Practicing mindfulness, taking breaks, engaging in relaxation techniques, seeking support when needed.
Navigating Organizational Change
Organizational changes, such as restructuring, new technologies, or mergers, can significantly impact middle managers and their teams. Effectively communicating these changes and building resilience are vital.
- Change management strategies: Communicating changes transparently, involving employees in the change process, providing training and support, fostering a culture of adaptability.
- Communicating change effectively: Using multiple communication channels, addressing employee concerns promptly, providing clear explanations of the reasons for change, outlining the impact on employees.
- Building resilience in teams: Promoting a positive attitude towards change, fostering a sense of teamwork and collaboration, recognizing and rewarding adaptability, providing support and resources.
- Fostering adaptability: Encouraging continuous learning, embracing new technologies, promoting innovation, creating a culture of experimentation and learning from mistakes.
Conclusion
Middle managers are the unsung heroes of business success and employee development. They serve as a critical link between leadership and the workforce, driving performance, fostering growth, and navigating organizational challenges. By recognizing their vital role and investing in their development, organizations can unlock greater business success and enhance employee engagement. Invest in your middle managers to unlock greater business success and employee development. Recognize the invaluable contribution of your middle managers—they are key to your company’s growth. Empowering your middle managers is empowering your entire organization.

Featured Posts
-
 Family Involvement In Hegseths Military Plan Disclosure Via Signal
Apr 22, 2025
Family Involvement In Hegseths Military Plan Disclosure Via Signal
Apr 22, 2025 -
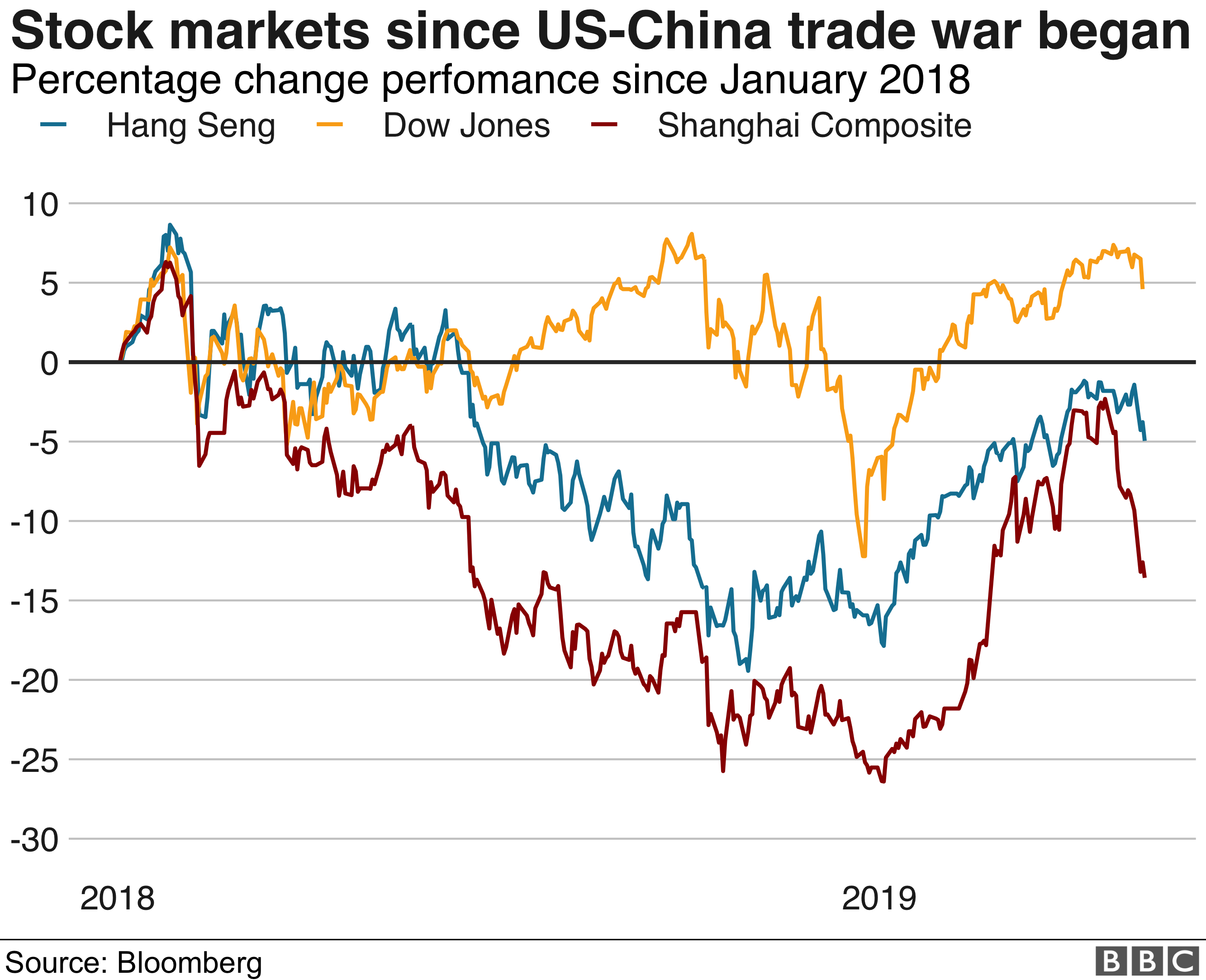 Stock Market Today Dow Futures Dollar And Trade War Impact
Apr 22, 2025
Stock Market Today Dow Futures Dollar And Trade War Impact
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Hollywood Shut Down Wga And Sag Aftra Strike Impact
Apr 22, 2025
Hollywood Shut Down Wga And Sag Aftra Strike Impact
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Bmw And Porsches China Challenges A Growing Trend In The Auto Industry
Apr 22, 2025
Bmw And Porsches China Challenges A Growing Trend In The Auto Industry
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Luxury Car Sales In China Examining The Difficulties Faced By Bmw And Porsche
Apr 22, 2025
Luxury Car Sales In China Examining The Difficulties Faced By Bmw And Porsche
Apr 22, 2025
