Analysis Of Vaccine Studies: HHS Appoints Vaccine Skeptic David Geier

Table of Contents
David Geier's Background and Vaccine-Related Publications
David Geier, a physician with a background in orthopedic surgery, has become a well-known voice questioning the safety and efficacy of certain vaccines. While his medical credentials are not disputed, his publications expressing skepticism towards vaccines have attracted significant scrutiny. His work often focuses on purported links between vaccines and various adverse health outcomes. A critical analysis of vaccine studies reveals that his approach often lacks the rigorous methodology expected in scientific research.
- Study X: Geier’s work often cites anecdotal evidence and focuses on isolated cases, neglecting larger-scale epidemiological studies that demonstrate the overwhelming safety of vaccines.
- Study Y: Many of his publications fail to establish causality, often conflating correlation with causation, a common pitfall in studies questioning vaccine safety. This failure to distinguish between correlation and causation is a significant flaw in his approach to analysis of vaccine studies.
- Methodological Flaws: Critiques of Geier's work consistently highlight methodological flaws, including small sample sizes, lack of appropriate control groups, and publication in journals with questionable peer-review processes. These flaws undermine the validity of his conclusions. A robust analysis of vaccine studies demands adherence to strict scientific standards.
The HHS Appointment and Public Reaction
Geier's appointment within the HHS sparked immediate and widespread concern among public health experts and organizations. The appointment was met with significant backlash from the scientific community, who pointed to Geier's history of publishing controversial and scientifically flawed studies.
- Public Health Concerns: The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and other leading public health organizations voiced concerns that Geier's appointment could erode public trust in vaccines.
- Scientific Community Response: Numerous scientists published articles and letters critiquing Geier’s work, highlighting its methodological flaws and the potential for his appointment to promote vaccine misinformation.
- Public Opinion: Public opinion polls consistently show that vaccine hesitancy remains a significant problem. The appointment fueled existing concerns and anxieties regarding vaccine safety.
This appointment carries significant implications for vaccine policy and public health initiatives. It has the potential to hinder efforts to increase vaccination rates and control the spread of preventable diseases.
Critical Analysis of Vaccine Studies Methodology
Rigorous methodology is paramount in vaccine research. High-quality studies are crucial for establishing both the safety and efficacy of vaccines. The analysis of vaccine studies must prioritize robust methodologies to ensure reliable and trustworthy conclusions.
- Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs): RCTs are the gold standard in evaluating vaccine efficacy, offering a strong foundation for analysis of vaccine studies. These studies randomly assign participants to either a vaccination group or a control group, minimizing bias and providing robust evidence.
- Meta-Analysis: Meta-analysis plays a crucial role in synthesizing findings from multiple studies, providing a more comprehensive and statistically powerful overview. This technique is essential for a thorough analysis of vaccine studies.
- Peer Review: The peer-review process is essential in ensuring the quality and validity of scientific publications. It involves expert scrutiny of research methods and findings before publication, a crucial element in any credible analysis of vaccine studies.
Impact on Public Trust and Vaccine Hesitancy
Geier's appointment, and the views he represents, have undoubtedly impacted public trust in vaccines. Misinformation readily spreads, particularly online, creating confusion and fear.
- Vaccine Hesitancy and Disease Outbreaks: Vaccine hesitancy is directly linked to outbreaks of preventable diseases. The spread of misinformation undermines public health efforts.
- Combating Misinformation: Effective communication strategies, focusing on evidence-based information from reputable sources, are crucial in addressing vaccine hesitancy.
- Trusted Sources of Information: The public needs access to reliable and understandable information from trusted sources, such as the CDC and WHO, to make informed decisions about vaccination.
Conclusion: Analysis of Vaccine Studies – A Call to Action
This article has highlighted the controversy surrounding David Geier's appointment to the HHS, the criticisms of his work, and the importance of rigorous methodology in the analysis of vaccine studies. The potential impact of misinformation on public trust in vaccines is undeniable. A critical analysis of vaccine studies reveals the importance of evidence-based decision-making, particularly regarding public health. We urge readers to seek information from reputable sources like the CDC and WHO, engage in critical thinking when evaluating health information, and actively promote vaccination to protect the health of individuals and communities. By undertaking a careful and thorough analysis of vaccine studies, we can promote informed choices and safeguard public health. The critical analysis of vaccine studies is crucial for maintaining trust in science and ensuring the well-being of society.

Featured Posts
-
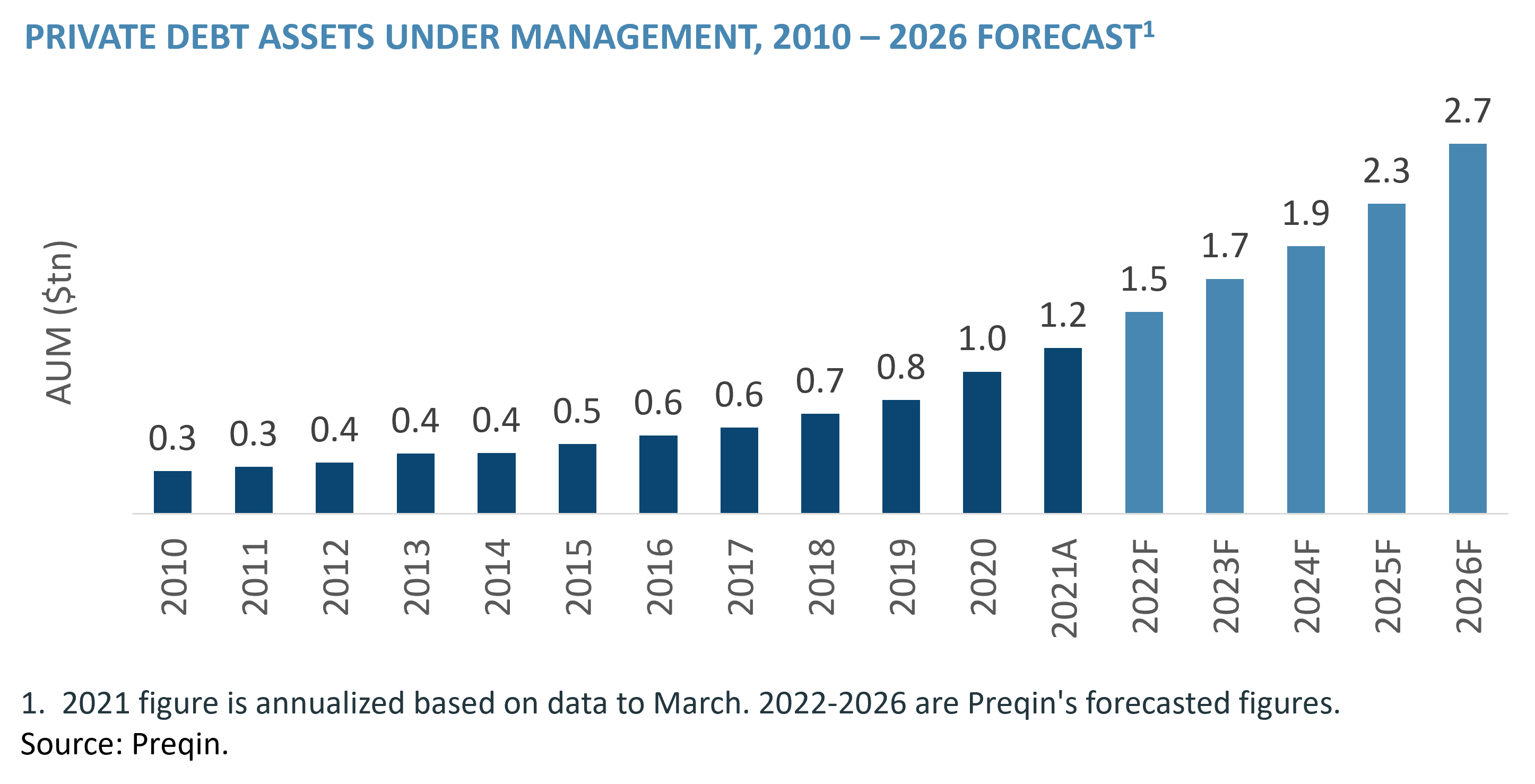 Private Credit Market Cracks A Weekly Analysis Of Recent Turmoil
Apr 27, 2025
Private Credit Market Cracks A Weekly Analysis Of Recent Turmoil
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Alejandro Tabilo Upsets Novak Djokovic In Monte Carlo
Apr 27, 2025
Alejandro Tabilo Upsets Novak Djokovic In Monte Carlo
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Bencic Triumphs First Wta Tournament Win Since Becoming A Mother
Apr 27, 2025
Bencic Triumphs First Wta Tournament Win Since Becoming A Mother
Apr 27, 2025 -
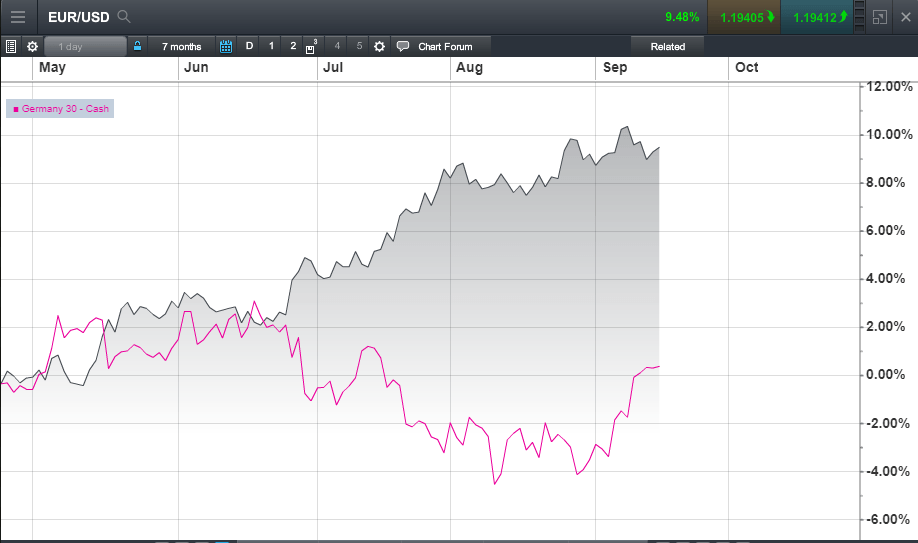 The Daxs Reaction To German Elections And Economic Indicators
Apr 27, 2025
The Daxs Reaction To German Elections And Economic Indicators
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Anti Trump Sentiment Divides Canada Albertas Exception
Apr 27, 2025
Anti Trump Sentiment Divides Canada Albertas Exception
Apr 27, 2025
