Grim Retail Sales Data: A Sign Of Looming Rate Cuts?

Table of Contents
Analyzing the Grim Retail Sales Data
Key Indicators of Weakness
The recent decline in retail sales paints a concerning picture of consumer spending. Several key sectors experienced significant drops. The apparel sector saw a particularly sharp decrease of 2.2%, while sales of consumer durables, such as appliances and electronics, fell by 1.8%. These retail sales declines are reflected across geographical regions, although some areas, such as rural communities, are experiencing more pronounced impacts. The overall retail sales decline is a critical economic indicator reflecting weakening consumer confidence and reduced purchasing power. Visual representations of this data, including charts and graphs, further illustrate the severity of the situation (Charts and graphs would be inserted here).
Underlying Causes of the Decline
Several factors have contributed to this grim retail sales data and the subsequent weakening of consumer spending:
- High Inflation and Reduced Consumer Purchasing Power: Persistently high inflation has eroded consumers' real incomes, leaving less disposable income for non-essential purchases. This is a significant driver of the retail sales decline.
- Rising Interest Rates and Decreased Borrowing: Increased interest rates have made borrowing more expensive, dampening consumer confidence and reducing spending on big-ticket items purchased with credit.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Ongoing supply chain bottlenecks continue to impact the availability of goods, leading to higher prices and reduced consumer choice.
- Geopolitical Uncertainty: Global political instability and economic uncertainty contribute to a climate of caution among consumers, leading to reduced spending.
Central Bank Response and the Probability of Rate Cuts
Central Bank Mandate and Current Monetary Policy
Central banks are tasked with maintaining price stability and promoting sustainable economic growth. Their primary tool for achieving this is monetary policy, which currently involves managing interest rates. Many central banks have recently pursued a policy of interest rate hikes to combat inflation. However, the grim retail sales data and the weakening economic outlook are prompting a reassessment of this strategy. Recent statements from central bank officials indicate a growing awareness of the softening economy.
The Case for Rate Cuts
The weak retail sales data significantly strengthens the case for monetary easing. Rate cuts could stimulate consumer spending by making borrowing cheaper and boosting consumer confidence. This, in turn, could help to prevent a deeper economic downturn. However, there are risks associated with rate cuts, primarily the potential for increased inflation if the economy is not as weak as the retail sales data suggests. Arguments for and against rate cuts include:
Arguments for Rate Cuts:
- Stimulates consumer spending and investment.
- Prevents a sharper economic contraction.
- Supports employment levels.
Arguments against Rate Cuts:
- Could exacerbate inflation.
- Could fuel asset bubbles.
- Might delay the return to price stability.
Alternative Scenarios and Economic Outlook
Scenario 1: Aggressive Rate Cuts
Significant interest rate reductions could lead to a rapid recovery in consumer spending and economic growth, but also risk fueling inflation and potentially creating asset bubbles.
Scenario 2: Gradual Rate Cuts
A more cautious approach with gradual rate cuts would offer a more measured response, minimizing the risks of fueling inflation, but potentially prolonging the economic slowdown.
Scenario 3: No Rate Cuts
Maintaining current interest rate levels could help control inflation, but might exacerbate the economic slowdown and lead to a more protracted period of weak growth and high unemployment. Careful economic forecasting and risk assessment are crucial in navigating these scenarios.
Conclusion: Grim Retail Sales Data and the Path Forward
In conclusion, the grim retail sales data points towards a potential economic slowdown, significantly increasing the likelihood of imminent rate cuts by central banks. The connection between weak consumer spending and central bank decision-making is undeniable. The various scenarios outlined highlight the complexity of the situation and the need for careful consideration of the risks and benefits of monetary policy adjustments. The economic outlook remains uncertain.
Stay tuned for updates on grim retail sales data and its impact on future rate cut decisions. Monitor our site for further analysis and insights into the evolving economic landscape and the implications for central bank policy.

Featured Posts
-
 Devin Williams Implosion Dooms Yankees In Loss To Blue Jays
Apr 28, 2025
Devin Williams Implosion Dooms Yankees In Loss To Blue Jays
Apr 28, 2025 -
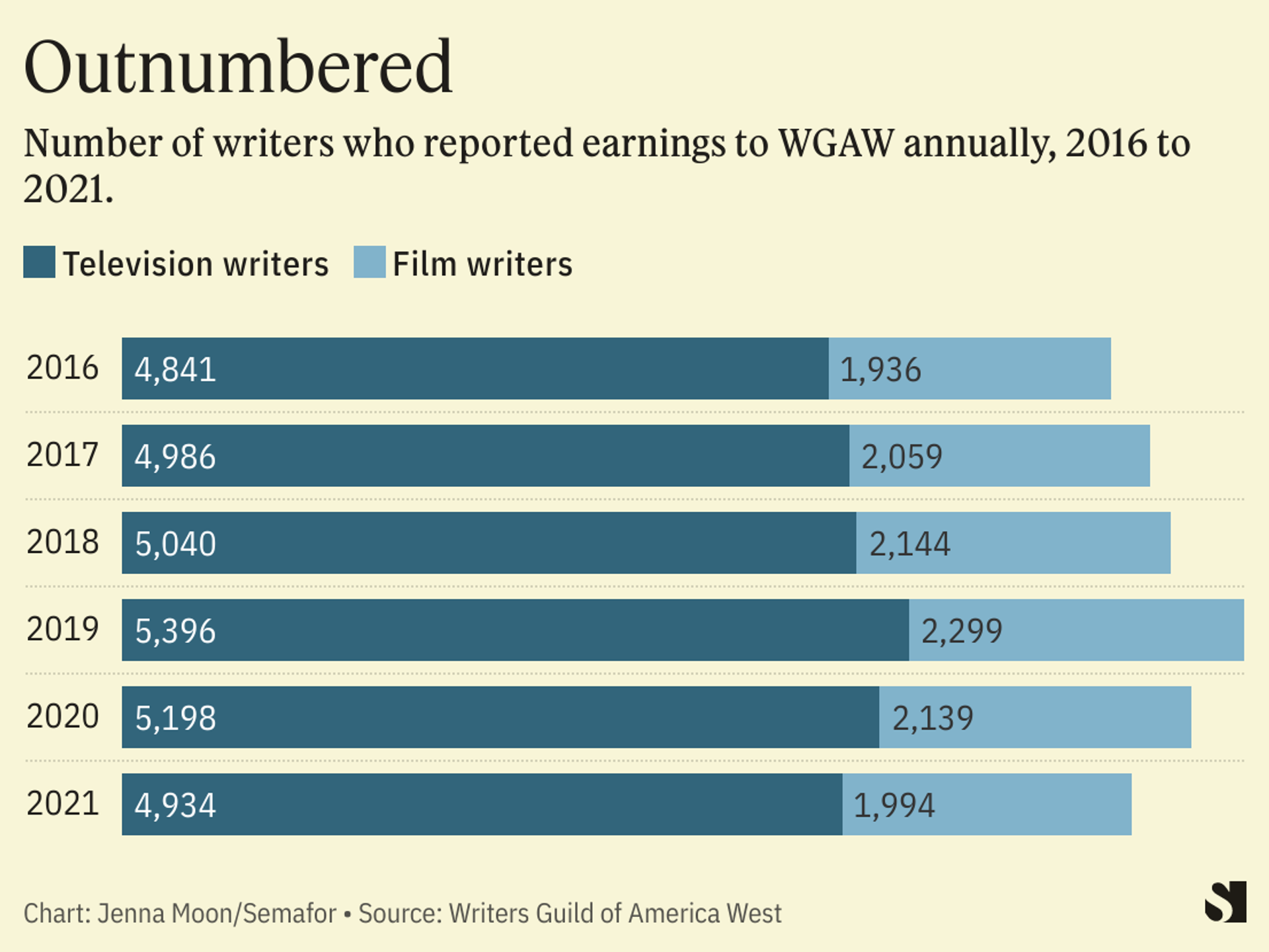 Actors And Writers Strike The Impact On Hollywood
Apr 28, 2025
Actors And Writers Strike The Impact On Hollywood
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Richard Jefferson Espn Promotion And Nba Finals Assignment Uncertainty
Apr 28, 2025
Richard Jefferson Espn Promotion And Nba Finals Assignment Uncertainty
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Nascar Jack Link 500 Props And Best Bets Talladega Superspeedway 2025 Predictions
Apr 28, 2025
Nascar Jack Link 500 Props And Best Bets Talladega Superspeedway 2025 Predictions
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Pandemic Era Covid Test Fraud Lab Owners Conviction
Apr 28, 2025
Pandemic Era Covid Test Fraud Lab Owners Conviction
Apr 28, 2025
