Assessing The Vulnerability Of China's Growth To Trade Wars
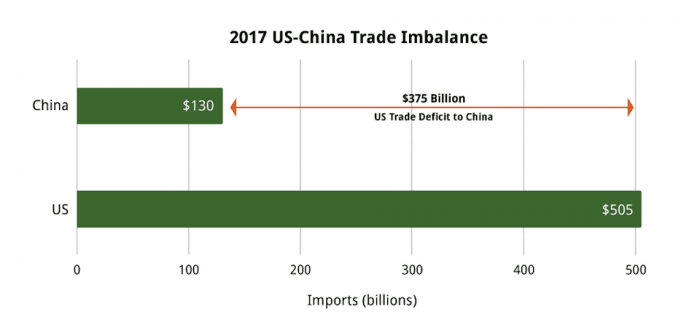
Table of Contents
China's Export Dependence and its Implications
China's historical reliance on exports as a primary engine of growth is undeniable. This export-oriented growth model, while successful for many years, has created a significant vulnerability to trade wars and protectionist measures. The implications of this dependence are far-reaching and necessitate a strategic reassessment of China's economic policies. Keywords: Export-oriented growth, export dependence, trade balance, export diversification, global value chains.
- High percentage of GDP derived from exports: For many years, a substantial portion of China's GDP was directly tied to its export performance. This creates a direct link between global trade tensions and domestic economic health.
- Concentration of exports in specific sectors: China's export basket isn't evenly diversified. A significant portion is concentrated in sectors like electronics, textiles, and manufacturing, making it susceptible to shocks affecting these particular industries.
- Dependence on specific export markets: Historically, China has had a strong dependence on specific markets, particularly the US. This concentration of export destinations heightens vulnerability to trade disputes with these major partners.
- Risks associated with reliance on global value chains: Participation in global value chains, while beneficial, increases interdependency and makes China vulnerable to disruptions in other countries' economies or policies.
- Strategies for export diversification and market penetration: To mitigate this risk, China needs to actively pursue export diversification strategies, focusing on new markets and product categories to reduce reliance on any single market or sector. This includes investing in branding and marketing efforts to promote Chinese goods globally.
The Impact of Trade Tariffs and Sanctions on Key Sectors
The US-China trade war, characterized by escalating trade tariffs and retaliatory measures, provided a stark illustration of the impact of trade conflicts on key sectors of the Chinese economy. Keywords: Trade tariffs, economic sanctions, retaliatory tariffs, impact on specific sectors, manufacturing, technology, agriculture.
- Impact on manufacturing industries: Many manufacturing sectors in China faced significant challenges due to tariffs, leading to reduced competitiveness in global markets and impacting employment.
- Impact on the technology sector (semiconductors, 5G): The technology sector, a crucial area of growth for China, was severely impacted by restrictions and sanctions, hindering its development and advancement in strategically important areas like semiconductors and 5G technology.
- Impact on agricultural exports and imports: Agricultural trade was also affected, impacting both exports and imports, leading to price fluctuations and supply chain disruptions.
- Effects on foreign investment and domestic production: Uncertainty caused by trade wars discouraged foreign investment and impacted domestic production decisions, slowing overall economic growth.
- Government responses to mitigate tariff impacts: The Chinese government implemented various measures, such as subsidies and tax incentives, to support affected industries and mitigate the negative impacts of tariffs.
Strengthening Domestic Demand and Reducing Reliance on Exports
To reduce its vulnerability to trade wars, China must focus on strengthening domestic demand and shifting towards a consumption-driven growth model. Keywords: Domestic consumption, consumption-driven growth, structural reform, income inequality, infrastructure investment.
- Policies to stimulate domestic consumption: Policies promoting higher disposable income, greater consumer confidence, and easier access to credit can significantly boost domestic consumption.
- Measures to address income inequality: Reducing income inequality is crucial for fostering a more robust middle class with greater purchasing power, driving up domestic consumption.
- Investment in infrastructure to boost domestic demand: Investment in infrastructure projects creates jobs, stimulates economic activity, and indirectly increases consumer spending.
- Promotion of domestic brands and products: Supporting and promoting domestic brands and products can help build national pride, enhance consumer confidence, and reduce reliance on foreign goods.
- Importance of structural reforms to foster balanced growth: Structural reforms are crucial to creating a more balanced and resilient economy less dependent on volatile global trade dynamics.
Building Supply Chain Resilience and Diversification
Building resilient and diversified supply chains is paramount for reducing China's vulnerability to trade wars and geopolitical risks. Keywords: Supply chain resilience, supply chain diversification, import diversification, geopolitical risks, regional trade agreements, RCEP.
- Diversification of import sources for critical inputs: China needs to diversify its import sources to reduce dependence on specific countries for critical inputs, lessening the impact of potential trade disruptions.
- Development of domestic supply chains: Investing in domestic production and technological self-sufficiency can significantly strengthen supply chain resilience and reduce reliance on foreign suppliers.
- Investment in technological self-sufficiency: China is actively investing in technology to reduce dependence on foreign technology and strengthen its domestic technological capabilities.
- Participation in regional trade agreements (e.g., RCEP): Participating in regional trade agreements like the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) can help diversify trade relationships and reduce dependence on any single market.
- Reducing reliance on specific suppliers: China is actively working to diversify its supplier base, reducing its reliance on any single supplier or country, thus mitigating risks from geopolitical instability or trade disputes.
Conclusion
China's economic growth, while remarkable, remains vulnerable to trade wars. Its dependence on exports, concentrated in specific sectors and markets, makes it susceptible to trade disruptions. However, China is actively pursuing strategies to mitigate these risks. These strategies include fostering domestic demand, diversifying its export markets, and strengthening its supply chain resilience. The effectiveness of these measures will determine the long-term impact of trade wars on China's economic trajectory. Continued monitoring of China’s economic policies and responses to future trade conflicts is crucial for assessing the ongoing vulnerability of China's growth to trade wars. Further research is needed to fully understand the long-term implications, both for China and the global economy. Analyzing the effectiveness of China's strategies to mitigate the impacts of future trade disputes will be vital in understanding the long-term implications for the global economy.

Featured Posts
-
 Turning Poop Into Podcast Gold How Ai Simplifies Scatological Document Analysis
Apr 22, 2025
Turning Poop Into Podcast Gold How Ai Simplifies Scatological Document Analysis
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Trumps Obamacare Supreme Court Defense A Boost For Rfk Jr
Apr 22, 2025
Trumps Obamacare Supreme Court Defense A Boost For Rfk Jr
Apr 22, 2025 -
 The Death Of Pope Francis A Global Loss
Apr 22, 2025
The Death Of Pope Francis A Global Loss
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Following The Karen Read Murder Trials A Year By Year Account
Apr 22, 2025
Following The Karen Read Murder Trials A Year By Year Account
Apr 22, 2025 -
 La Wildfires Exploring The Ethics Of Disaster Betting Markets
Apr 22, 2025
La Wildfires Exploring The Ethics Of Disaster Betting Markets
Apr 22, 2025
